Posts Tagged ‘ascites’
What Is Ascites?
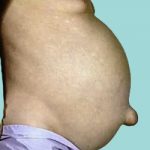
What is ascites? Ascites is the accumulation of fluid (usually serous fluid which is a pale yellow and clear fluid) that accumulates in the abdominal (peritoneal) cavity. The abdominal cavity is located below the chest cavity, separated from it by the diaphragm. Ascitic fluid can have many sources such as liver disease, cancers, congestive heart…
Read MoreWhat Is Ascites and Edema?
Ascites and Edema In patients with chronic diseases of the liver, fibrosis (scarring) of the liver often occurs. When the scarring becomes advanced, the condition is called cirrhosis of the liver. Ascites is excessive fluid that accumulates in the abdominal (peritoneal) cavity. It is a complication of cirrhosis and appears as an abdominal bulge. The…
Read MoreEnd-Stage Liver Disease in HIV Disease
This article is a wonderful description of cirrhosis and it’s major symptoms. Everyone with cirrhosis should read this and learn from it. Craig Liver disease is the most common non–AIDS-related cause of mortality in HIV-infected patients. HIV-infected patients with chronic liver disease progress more rapidly to cirrhosis, and those with hepatitis B virus or hepatitis…
Read MoreComplications of Cirrhosis: Ascites, Hepatic Encephalopathy, and Variceal Hemorrhage
Complications of Cirrhosis Anuja Choure William D. Carey Ascites Definition and Etiology Ascites is defined as the accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity. It is a common clinical finding, with various extraperitoneal and peritoneal causes (Box 1), but it most often results from liver cirrhosis. The development of ascites in a cirrhotic patient generally…
Read MoreWhat Are the Treatments for Portal Hypertension?
What Are the Treatments for Portal Hypertension? The portal vein carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract to the liver. If this vein becomes blocked by cirrhosis which is a scarring of the liver or by a blood clot the pressure inside the vein increases. This increase in pressure is called portal hypertension. When blood flow…
Read MoreWhat is Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis?
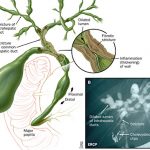
What Is Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Primary sclerosing cholangitis is inflammation with progressive scarring and narrowing of the bile ducts in and outside the liver. Eventually, the ducts become blocked and then obliterated. Cirrhosis, liver failure, and sometimes bile duct cancer develop. * Symptoms begin gradually and include worsening fatigue, itchiness, and, later, jaundice. * An…
Read MoreHepatorenal syndrome (HRS)
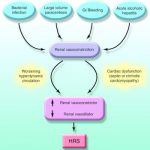
Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) In some patients, type 1 HRS develops spontaneously without any identifiable precipitating factor, whereas in others it can occur in close association with systemic bacterial infections, in particular SBP, acute alcoholic hepatitis, and large volume paracentesis without albumin expansion. SBP precipitates type 1 HRS in approximately 20% of cases despite appropriate treatment…
Read MoreAlcoholic cirrhosis patients had high prevalence of complications at diagnosis
Complications at Diagnosis April 27, 2010 − Wiley-Blackwell A recent study by Danish researchers discovered patients with alcoholic cirrhosis had a high prevalence of complications at the time of the disease diagnosis. Researchers noted that complications, such as ascites (excessive fluid in the abdomen), were predictors of mortality, but did not develop in a predictable…
Read MoreTIPS in the Management of Refractory Ascites
TIPS in the Management of Refractory Ascites Kevin B. Mercure, M.D. Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center Department of Internal Medicine Resident Grand Rounds April 6, 2004 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ASCITES Ascites is a collection of excess fluid in the peritoneal cavity. The pathogenesis of ascites in patients with cirrhosis involves several mechanisms. Portal hypertension results…
Read MoreExams and Tests
Exams and Tests Cirrhosis is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when inflammation and scarring damage the liver. A physical examination and medical history will be done first to assess symptoms of liver disease, to see whether liver disease is severe enough to cause signs of cirrhosis, and to help determine possible causes of liver…
Read More