The Wiki

The Wiki contains all the articles on the web site. The articles are put into categories and 'tagged' for easier searching.
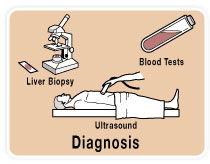
Exams and Tests Cirrhosis is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when inflammation and scarring damage the liver. A physical examination and medical history will be done first to assess symptoms of liver disease, to see whether liver disease is severe enough to cause signs of cirrhosis, and to help determine possible causes of liver…
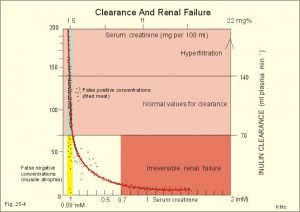
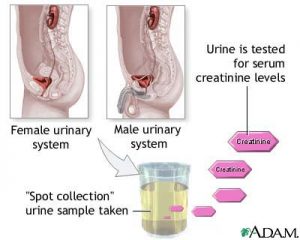
What is creatinine? Creatinine is a chemical waste molecule that is generated from muscle metabolism. Creatinine is produced from creatine, a molecule of major importance for energy production in muscles. Approximately 2% of the body’s creatine is converted to creatinine every day. Creatinine is transported through the bloodstream to the kidneys. The kidneys filter out…
Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance Creatinine and creatinine clearance tests measure the level of the waste product creatinine in your blood and urine. These tests tell how well your kidneys are working. The substance creatine is formed when food is changed into energy through a process calledmetabolism. Creatine is broken down into another substance called creatinine,…
Complications and Treatment JOEL J. HEIDELBAUGH, M.D., and MARYANN SHERBONDY, M.D. University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan Major complications of cirrhosis include ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, hepatic encephalopathy, portal hypertension, variceal bleeding, and hepatorenal syndrome. Diagnostic studies on ascitic fluid should include a differential leukocyte count, total protein level, a serum-ascites albumin gradient,…
Diagnosis and Evaluation JOEL J. HEIDELBAUGH, M.D., and MICHAEL BRUDERLY, M.D. University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan This is part I of a two-part article on cirrhosis and chronic liver failure. Part II, “Complications and Treatment,” appears in this issue of AFP on page 767. Cirrhosis and chronic liver failure are leading causes…
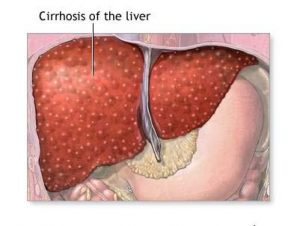
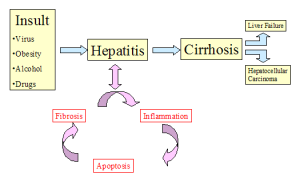
Symptoms of Cirrhosis of the Liver Cirrhosis of the liver refers to a condition characterized by the development of fibrous scar tissue on the liver and regenerative nodules or lumps. This chronic liver disease leads to progressive deterioration of liver function… Liver function is vital to detoxification and protein synthesis, within the human body. It…
What happens next?? A question asked by most people who initially get diagnosed with this disease is ‘Ok, so what happens next???’ Here are some answers, this is a good primer on what to do next and what to expect. Treatment Overview Cirrhosis is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when inflammation and scarring damage…
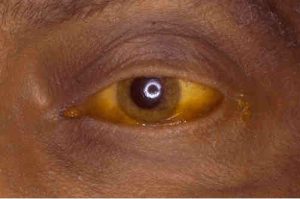
Liver Diseases and their Symptoms Alagille Syndrome – an inherited disorder characterized by a progressive loss of the bile ducts within the liver and narrowing of bile ducts outside the liver over the first year of life. Symptoms include jaundice, pale, loose stools and poor growth within the first three months of life. Alpha 1…
Cirrhosis Many Causes The onset of cirrhosis is often ‘silent’ with few specific symptoms…” Basic facts about the liver Your liver, the largest organ in your body, weighs about three pounds and is roughly the size of a football. It lies in the upper right side of your abdomen situated mostly under the lower ribs.…
Cachexia Catabolic wasting or cachexia is a clinical wasting syndrome that is characterized by unintended and progressive weight loss, weakness, and low body fat and muscle. At least 5% of body weight is lost. Cachexia is not caused by poor appetite and nutritional intake, but rather by a metabolic state in which a “breaking down”…